The RSA algorithm, named after its inventors Rivest Shamir Adleman, is a cornerstone of modern cryptography. It is an asymmetric encryption algorithm, meaning it uses two different keys for encryption and decryption. Public key is used for encryption and private key is used for decryption. This article delves into the use of RSA algorithm explaining how to use rsa encryption algorithm in java with steps involved in key generation, encryption, and decryption processes, and providing examples for better understanding.
1. Introduction to RSA Algorithm
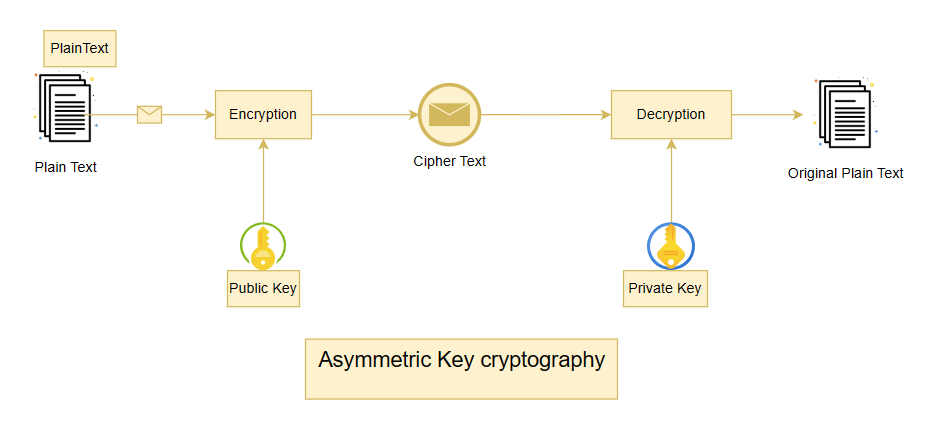
1.1 What is Public-Key Cryptography?
Public-key cryptography, also known as asymmetric cryptography, involves the use of two keys: a public key and a private key. The public key is used for encryption, while the private key is used for decryption. This ensures that even if the public key is widely known, only the holder of the private key can decrypt the messages.
1.2 Importance of RSA
RSA is widely used in securing data transmission, particularly for sensitive data. Its security relies on the mathematical difficulty of factoring large prime numbers, making it a robust choice for encryption.
2. RSA Algorithm Explained
2.1 Key Generation
The RSA algorithm involves the generation of two keys: a public key and a private key. This process includes several mathematical steps:
2.1.1 Selecting Prime Numbers
Choose two large prime numbers, p and q.
2.1.2 Calculating Modulus n
Multiply these numbers to find n:
n = p \times q
The modulus n is used in both the public and private keys.
2.1.3 Computing Euler’s Totient Function ϕ(n)
phi(n) = (p - 1) \times (q - 1)
2.1.4 Choosing the Public Exponent e
Select an integer e such that 1<e<ϕ(n) and gcd(e,ϕ(n))=1 The pair (e, n) forms the public key.
1 < e < \phi(n) \quad \text{and} \quad \gcd(e, \phi(n)) = 1
2.1.5 Determining the Private Exponent d
Calculate the private exponent d such that
d \times e \mod \phi(n) = 1
The pair (d, n) forms the private key.
2.2 Encryption Process
To encrypt a message mmm:
- Convert the plaintext message mmm into an integer less than n.
- Compute the ciphertext c using the formula:
c = m^e \mod n
2.3 Decryption Process
To decrypt a ciphertext c:
- Compute the plaintext message musing the formula: m
m = c^d \mod n
3. Examples of RSA Algorithm
3.1 Example 1: Basic RSA Encryption and Decryption
Let’s walk through a basic example using small prime numbers for simplicity.
3.1.1 Key Generation
Select primes ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
Calculate ![]() .
.
Compute ![]() .
.
Choose ![]() (since
(since ![]() ).
).
Determine ![]() such that
such that ![]() . Here,
. Here, ![]() .
.
The public key is ![]() and the private key is
and the private key is ![]() .
.
3.1.2 Encryption
Encrypt the plaintext message m=9
c = 9^7 \mod 77 = 37
3.1.3 Decryption
Decrypt the ciphertext c=37
m = 37^{43} \mod 77 3.2 Example 2: Finding the Private Key
Given primes ![]() and
and ![]() , and a public key
, and a public key ![]() , find the private key.
, find the private key.
Calculate ![]() .
.
Compute ![]() .
.
Find ![]() such that
such that ![]() . Here,
. Here, ![]() .
.
The private key is ![]() .
.
3.3 Example 3: Encrypting a Larger Message
Given primes ![]() and
and ![]() , encrypt the message
, encrypt the message ![]() .
.
Calculate ![]() .
.
Compute ![]() .
.
Choose ![]() (since
(since ![]() ).
).
Determine ![]() such that
such that ![]() . Here,
. Here, ![]() .
.
Encrypt the plaintext message ![]() :
: ![]() .
.
Decrypt the ciphertext ![]() :
: ![]() .
.
4. RSA encryption java
4.1 Generating Key Pairs
Using the Java KeyPairGenerator class, we can generate RSA key pairs the code below initializes a KeyPairGenerator object for the RSA algorithm with a key size of 2048 bits, generating a key pair that includes a private key and a public key using the generateKeyPair() method. The private key, retrieved using getPrivate(), represents the secure component of the key pair used for decrypting data, while the public key, obtained with getPublic(), serves for encrypting data and can be shared openly. This approach is foundational in asymmetric cryptography, where the encryption and decryption keys are different, enhancing security by keeping the private key confidential while allowing anyone with the public key to encrypt data that can only be decrypted by the owner of the private key.
KeyPairGenerator generator = KeyPairGenerator.getInstance("RSA");
generator.initialize(2048);
KeyPair pair = generator.generateKeyPair();
PrivateKey privateKey = pair.getPrivate();
PublicKey publicKey = pair.getPublic();
4.2 Encrypting and Decrypting Strings
4.2.1 Encryption
This Java code below illustrates how to encrypt a message using the RSA algorithm. First, it initializes a Cipher object for RSA encryption mode and sets its encryption key to the provided publicKey. Then, the secretMessage is converted to a byte array using UTF-8 encoding. The encryptCipher.doFinal() method encrypts the byte array, producing encryptedMessageBytes. Finally, the encrypted bytes are encoded to a Base64 string using Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(), resulting in encodedMessage, which can be safely transmitted or stored. This process ensures secure data transmission and storage by converting plaintext into encrypted data that can only be decrypted with the corresponding private key.
Cipher encryptCipher = Cipher.getInstance("RSA");
encryptCipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, publicKey);
byte[] secretMessageBytes = secretMessage.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
byte[] encryptedMessageBytes = encryptCipher.doFinal(secretMessageBytes);
String encodedMessage = Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(encryptedMessageBytes);
4.2.2 Decryption
This code below demonstrates how to decrypt a message using the RSA algorithm. It begins by initializing a Cipher object for RSA decryption mode and setting its decryption key to the provided privateKey. Then, the encrypted message bytes (previously obtained through encryption) are passed to decryptCipher.doFinal(), which decrypts them, resulting in decryptedMessageBytes. Finally, these decrypted bytes are converted back into a string using UTF-8 encoding with new String(decryptedMessageBytes, StandardCharsets.UTF_8), yielding decryptedMessage. This process ensures that the encrypted message, encoded in Base64 or another format, can be securely decrypted back to its original plaintext form using the appropriate private key.
Cipher decryptCipher = Cipher.getInstance("RSA");
decryptCipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, privateKey);
byte[] decryptedMessageBytes = decryptCipher.doFinal(encryptedMessageBytes);
String decryptedMessage = new String(decryptedMessageBytes, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
4.3 Encrypting and Decrypting Files
4.3.1 Encryption
This Java code below shows how to encrypt a file using the RSA algorithm. Initially, it reads all bytes from the specified tempFile and stores them in the byte array fileBytes. Then, it initializes a Cipher object for RSA encryption mode and sets its encryption key to the provided publicKey. The fileBytes are encrypted using encryptCipher.doFinal(), producing encryptedFileBytes. Finally, the encrypted bytes are written back to the tempFile using a FileOutputStream, thereby encrypting the contents of the file with RSA encryption and overwriting the original file with the encrypted data.
byte[] fileBytes = Files.readAllBytes(tempFile);
Cipher encryptCipher = Cipher.getInstance("RSA");
encryptCipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, publicKey);
byte[] encryptedFileBytes = encryptCipher.doFinal(fileBytes);
try (FileOutputStream stream = new FileOutputStream(tempFile.toFile())) {
stream.write(encryptedFileBytes);
}
4.3.2 Decryption
This Java code below demonstrates how to decrypt a file encrypted with the RSA algorithm. Initially, it reads all bytes from the specified tempFile (which contains the encrypted file data) and stores them in the byte array encryptedFileBytes. Then, it initializes a Cipher object for RSA decryption mode and sets its decryption key to the provided privateKey. The encryptedFileBytes are decrypted using decryptCipher.doFinal(), resulting in decryptedFileBytes. Finally, the decrypted bytes are written back to the tempFile using a FileOutputStream, effectively decrypting the contents of the file with RSA decryption and overwriting the original encrypted file with the decrypted data.
byte[] encryptedFileBytes = Files.readAllBytes(tempFile);
Cipher decryptCipher = Cipher.getInstance("RSA");
decryptCipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, privateKey);
byte[] decryptedFileBytes = decryptCipher.doFinal(encryptedFileBytes);
try (FileOutputStream stream = new FileOutputStream(tempFile.toFile())) {
stream.write(decryptedFileBytes);
}
5. RSA algorithm java Implementation
Below is an example of how to implement RSA encryption and decryption in Java.
package asymmetricCryptography;
import javax.crypto.Cipher;
import java.security.KeyPair;
import java.security.KeyPairGenerator;
import java.security.PrivateKey;
import java.security.PublicKey;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class RsaExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// Ask for the user input
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a message to encrypt");
String userMessage = input.nextLine();
// Second step: Generate a rsa key pair
KeyPair keyPair = generateRsaKeyPair();
PublicKey publicKey = keyPair.getPublic();
PrivateKey privateKey = keyPair.getPrivate();
// Step 3: Implement an encryption
byte [] cipherText = encrypt(userMessage, publicKey);
// Step 4: Print the cipher Text
System.out.println("Original Text is: " + userMessage);
System.out.println("Cipher text is: " + new String(cipherText));
// Step 4: Implement decryption as well
String originalMessage = decryption(cipherText, privateKey);
System.out.println("Decrypted text from cipher text is " + originalMessage);
}
public static KeyPair generateRsaKeyPair() throws Exception {
KeyPairGenerator keyPairGenerator = KeyPairGenerator.getInstance("RSA");
// Define the size of a key
keyPairGenerator.initialize(2048);
return keyPairGenerator.generateKeyPair();
}
public static byte [] encrypt(String message, PublicKey publicKey) throws Exception{
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("RSA");
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, publicKey);
return cipher.doFinal(message.getBytes());
}
public static String decryption(byte [] cipherText, PrivateKey privateKey) throws Exception {
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("RSA");
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, privateKey);
byte [] decryptedOriginalArray = cipher.doFinal(cipherText);
return new String(decryptedOriginalArray);
}
}
This above Java code snippet demonstrates how to generate an RSA key pair, encrypt a message using the public key, and then decrypt it using the private key.
- The code starts by asking the user to input a message to be encrypted
- .It generates an RSA key pair using the
generateRsaKeyPair()method, initializing a KeyPairGenerator with RSA algorithm and a 2048-bit key size. - The key pair includes a public key (
PublicKey) and a private key (PrivateKey).Encryption is performed using theencryptmethod, encrypting the user’s input message with the RSA algorithm and the obtained public key. - The encrypted message (cipher text) is stored in a byte array.The original message and corresponding cipher text (encrypted message) are printed to the console.Decryption is demonstrated using the
decryptionmethod, decrypting the cipher text back to the original message using the private key. - The decrypted original message is printed to the console, confirming the successful encryption and decryption process.
6. Advantages and Applications of RSA Algorithm
RSA’s robustness comes from the difficulty of factoring large composite numbers which is the basis of its security. The versatility of RSA algorithm spans on various domains such as
- Secure Communication: Facilitating secure data exchange, especially in online transactions and communication platforms.
- Digital Signatures: Enabling digital signatures for authentication and non-repudiation.
- Key Exchange: Playing a vital role in key exchange protocols like SSL/TLS.
7. Video Tutorial on RSA algorithm in java
In this comprehensive video tutorial, you will gain a deep understanding of how to utilize the RSA algorithm effectively in Java. The tutorial will walk you through the process of generating a key pair, encrypting a message using the generated keys, and then decrypting the encrypted message step by step, providing you with a solid foundation in RSA encryption and decryption techniques within the Java programming environment
7. Advantage and disadvantage of RSA algorithm
The following are the advantage and disadvantages of using RSA algorithm.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Security: Security wise RSA algorithm is highly secure and widely used for secure data transmission. | Slow processing speed: RSA algorithm is slower, especially with large data. |
| Public-key cryptography: RSA uses separate keys for encryption and decryption which enhance the security. | Large key size: Requires significant computational and storage resources. |
| Key exchange: Facilitates secure key exchange without transmitting the key over the network. | Vulnerability to side-channel attacks: Prone to attacks using leaked information. |
| Digital signatures: Enables reliable digital signatures and verification using public/private keys. | Limited use in some applications: Not ideal for constant large data encryption. |
| Speed: RSA is suitable for real-time applications due to its efficiency. | Complexity: Requires understanding of sophisticated mathematical concepts. |
| Widely used: Extensively developed and applied in fields like online banking and secure communications. | Key Management: Secure private key administration is crucial but challenging. |
| Vulnerability to Quantum Computing: Potential decryption threat from quantum computers |
